How to randomize treatments using R?
Setting up experimental design according to your experiment goal is the first step to achieve your experiment’s success. In Agronomy studies, experimental design involves the combination of treatments deployed in the field, and these treatments should be randomized. Randomization is important in experimental design as it helps our experiments avoid biases due to physical or biological factors. Of course, there are no specific, unconditional rules for randomization. In a very old-fashioned way, you can write treatment numbers on paper, and then choose each paper as if drawing lots. However, we’re researchers and we can use more advanced ways to randomize our treatments. Today, I’ll introduce how to randomize treatments using R according to each experimental design.
1) One factor without block (Completely Randomized Design)
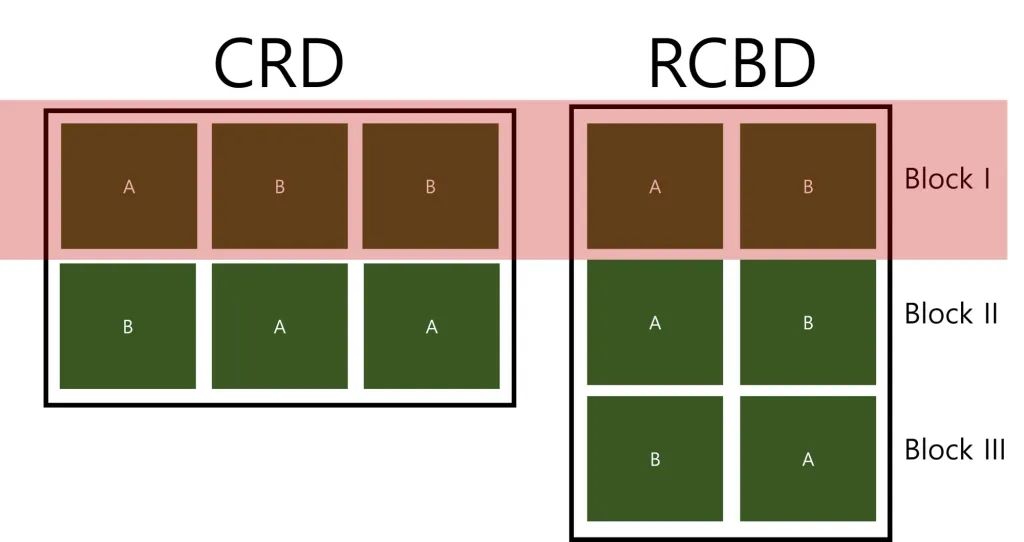
In Completely Randomized Design (CRD), experimental units are randomly assigned to different treatment groups. Each treatment group represents a level of the independent variable being tested. In a CRD, replicates are not considered as blocks. If replicates are considered as blocks, it will be a Randomized Complete Block Design (RCBD). The differences between CRD and RCBD will be summarized below my post.
■ How to calculate pooled variance when including block in the experimental design?
Let’s say there is one factor, ‘nitrogen’, and the experimental design was Completely Randomized Design (CRD), and there were 4 replicates.
df = tibble::tibble(
N_rate=c("0N", "50N", "100N", "150N"),
`Rep 1`=seq(101, 104, by=1),
`Rep 2`=seq(201, 204, by=1),
`Rep 3`=seq(301, 304, by=1),
`Rep 4`=seq(401, 404, by=1),
)
df
N_rate Rep 1 Rep 2 Rep 3 Rep 4
0N 101 201 301 401
50N 102 202 302 402
100N 103 203 303 403
150N 104 204 304 404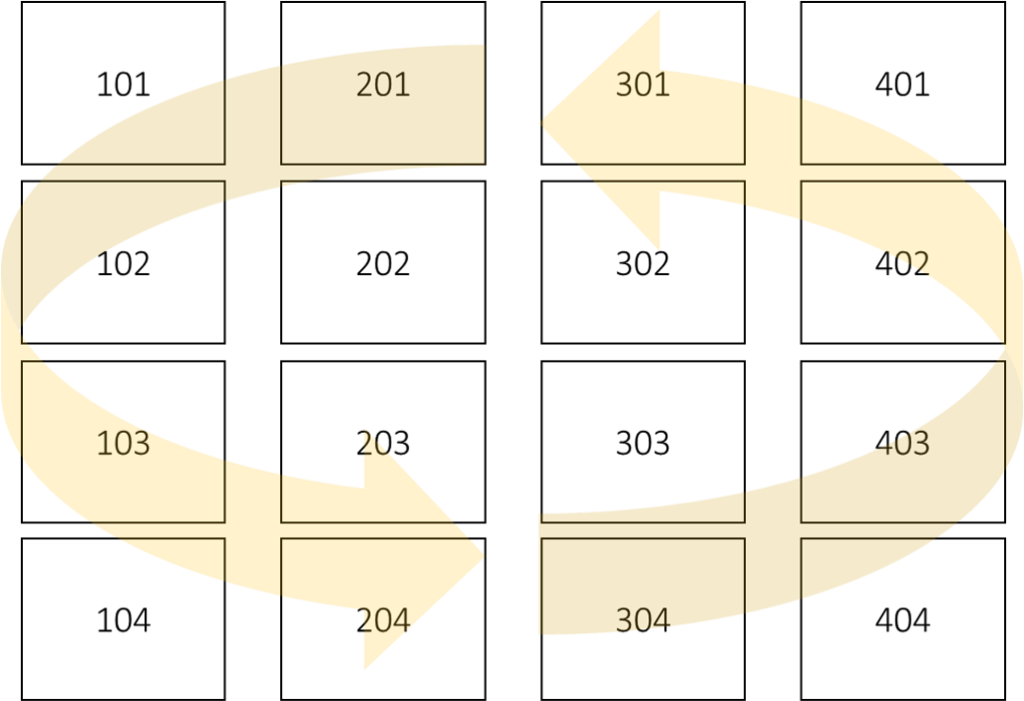
I’ll randomize treatments using CRD.
library(dplyr)
df_randomized= df %>%
pivot_longer(-N_rate, names_to= "Replicate",
values_to= "Value") %>%
mutate(Value= sample(Value)) %>%
pivot_wider(names_from= Replicate, values_from= Value)
df_randomized
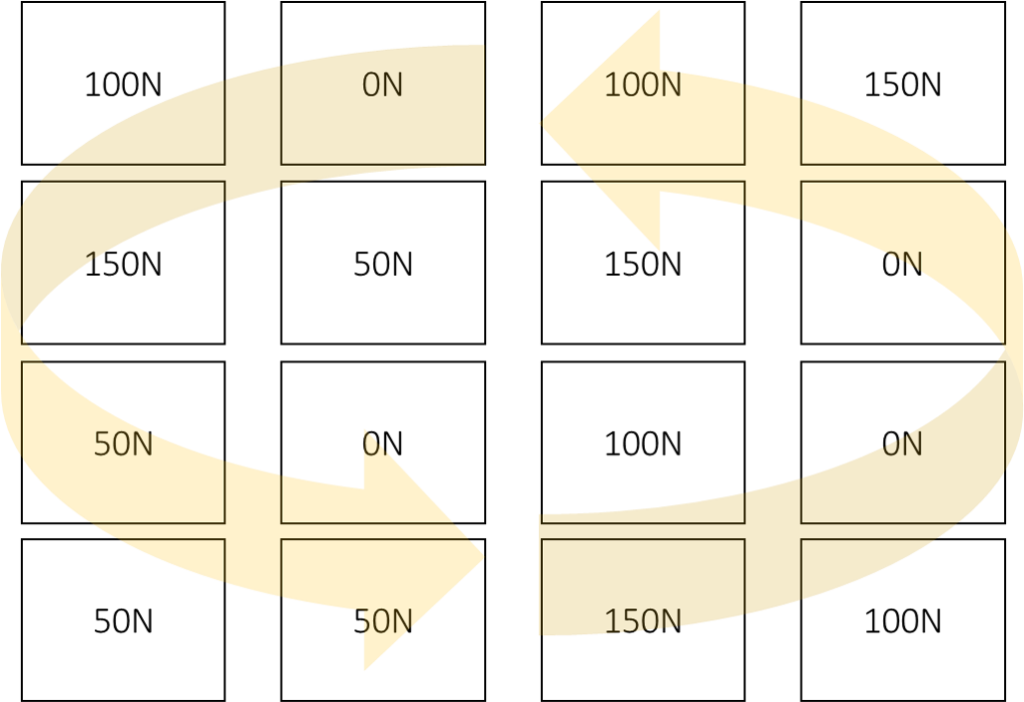
N_rate Rep 1 Rep 2 Rep 3 Rep 4
0N 203 201 402 403
50N 202 104 103 204
100N 101 301 303 404
150N 302 401 304 102Based on this randomization, the experimental design will be as follows: all treatments will be randomized within the entire plot.
2) Two factors without block (Completely Randomized Design)
Now, while maintaining CRD, there are two factors to consider: variety and nitrogen.
df = tibble::tibble(
Variety= rep(c("CV1", "CV2"), each= 4L),
N_rate= rep(c("0N", "50N", "100N", "150N"), 2),
`Rep 1`= seq(101, 108, by= 1),
`Rep 2`= seq(201, 208, by= 1),
`Rep 3`= seq(301, 308, by= 1),
`Rep 4`= seq(401, 408, by= 1),
)
df
Variety N rate Rep 1 Rep 2 Rep 3 Rep 4
CV1 0N 101 201 301 401
CV1 50N 102 202 302 402
CV1 100N 103 203 303 403
CV1 150N 104 204 304 404
CV2 0N 105 205 305 405
CV2 50N 106 206 306 406
CV2 100N 107 207 307 407
CV2 150N 108 208 308 408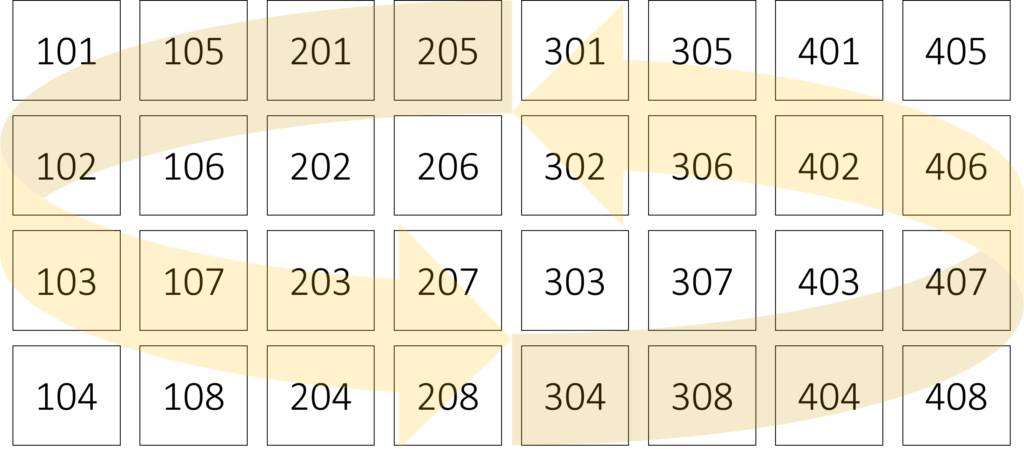
I’ll randomize treatment combination (i.e., CV1 N0) using CRD, employing the following code.
library(dplyr)
library(tidyr)
df_randomized= df %>%
pivot_longer(-c(Variety, N_rate), names_to= "Replicate",
values_to= "Value") %>%
mutate(Value= sample(Value)) %>%
pivot_wider(names_from= Replicate, values_from= Value)
df_randomized
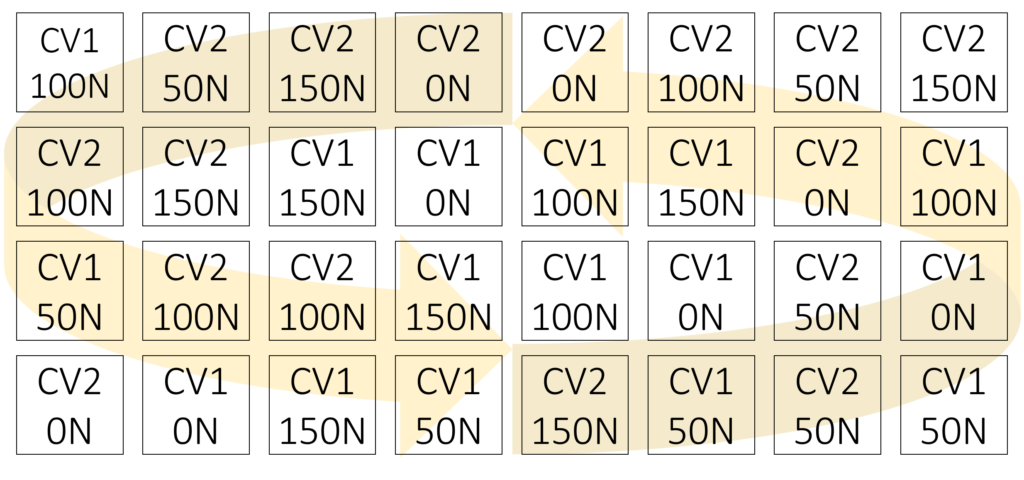
Variety N_rate Rep 1 Rep 2 Rep 3 Rep 4
CV1 0N 108 407 307 206
CV1 50N 103 308 208 408
CV1 100N 406 303 302 101
CV1 150N 207 202 204 306
CV2 0N 104 205 402 301
CV2 50N 401 404 105 403
CV2 100N 203 305 107 102
CV2 150N 304 405 106 201Based on this randomization, the experimental design will be as follows: all treatment combinations will be randomized within the entire plot.
3) One factor with block (Randomized Complete Block Design)
Since we are transitioning to RCBD, the experimental design will involve replicates as blocks.
df = tibble::tibble(
N_rate = c("0N", "50N", "100N", "150N"),
`Rep 1` = seq(101, 104, by = 1),
`Rep 2` = seq(201, 204, by = 1),
`Rep 3` = seq(301, 304, by = 1),
`Rep 4` = seq(401, 404, by = 1),
)
df
N_rate Rep 1 Rep 2 Rep 3 Rep 4
0N 101 201 301 401
50N 102 202 302 402
100N 103 203 303 403
150N 104 204 304 404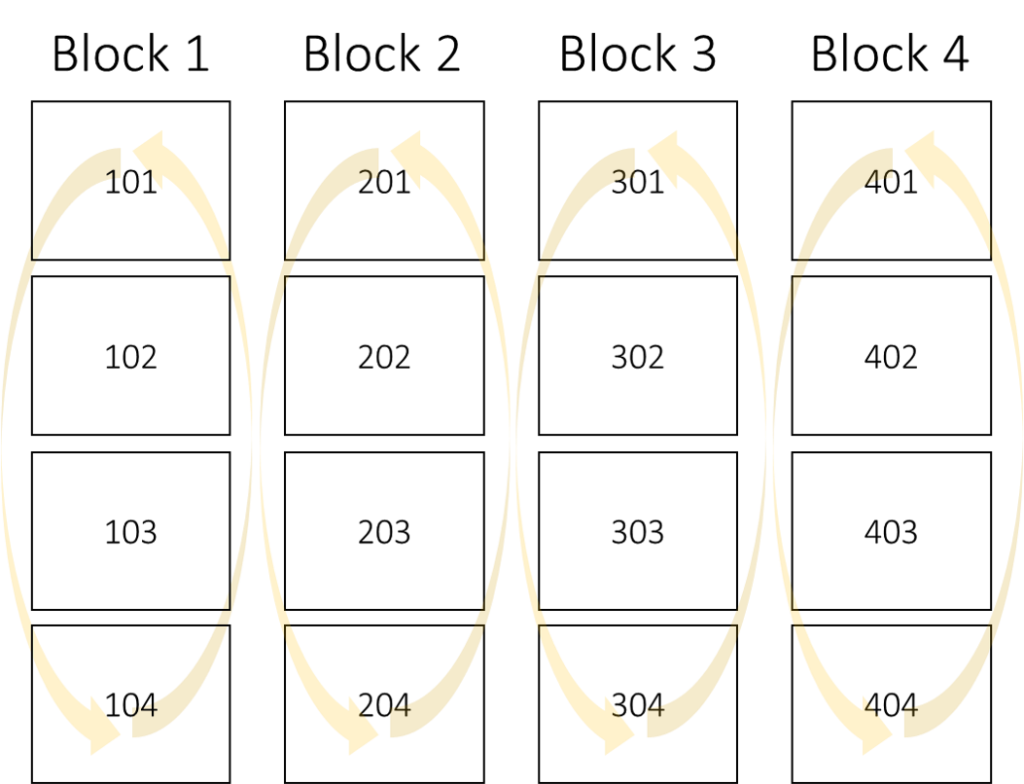
In contrast to CRD, in RCBD, randomization occurs within each block, whereas previously it was randomized within the entire plot.
library(dplyr)
set.seed(100)
df_randomized=df %>%
group_by() %>%
mutate(across(starts_with("Rep"), ~sample(.))) %>%
ungroup()
df_randomized
N_rate Rep 1 Rep 2 Rep 3 Rep 4
0N 102 203 304 402
50N 103 201 303 403
100N 104 202 302 404
150N 101 204 301 401
4) Two factors with block (Randomized Complete Block Design)
Now, while maintaining RCBD, there are two factors to consider: variety and nitrogen.
df = tibble::tibble(
Variety= rep(c("CV1", "CV2"), each= 4L),
N_rate= rep(c("0N", "50N", "100N", "150N"), 2),
`Rep 1`= seq(101, 108, by= 1),
`Rep 2`= seq(201, 208, by= 1),
`Rep 3`= seq(301, 308, by= 1),
`Rep 4`= seq(401, 408, by= 1),
)
df
Variety N rate Rep 1 Rep 2 Rep 3 Rep 4
CV1 0N 101 201 301 401
CV1 50N 102 202 302 402
CV1 100N 103 203 303 403
CV1 150N 104 204 304 404
CV2 0N 105 205 305 405
CV2 50N 106 206 306 406
CV2 100N 107 207 307 407
CV2 150N 108 208 308 408
I’ll randomize treatment combination (i.e., CV1 N0) using RCBD, employing the following code.
library(dplyr)
set.seed(100)
df_randomized=df %>%
group_by() %>%
mutate(across(starts_with("Rep"), ~sample(.))) %>%
ungroup()
df_randomized
Variety N rate Rep 1 Rep 2 Rep 3 Rep 4
CV1 0N 102 207 307 402
CV1 50N 107 206 308 401
CV1 100N 106 208 303 408
CV1 150N 103 204 302 403
CV2 0N 101 203 301 404
CV2 50N 108 202 306 406
CV2 100N 105 205 304 405
CV2 150N 104 201 305 407Based on this randomization, the experimental design will be as follows: all treatment combinations will be randomized within the block.

5) Split-plot design
df = tibble::tibble(
Variety= rep(c("CV1", "CV2"), each= 4L),
N_rate= rep(c("0N", "50N", "100N", "150N"), 2),
`Rep 1`= seq(101, 108, by= 1),
`Rep 2`= seq(201, 208, by= 1),
`Rep 3`= seq(301, 308, by= 1),
`Rep 4`= seq(401, 408, by= 1),
)
df
Variety N rate Rep 1 Rep 2 Rep 3 Rep 4
CV1 0N 101 201 301 401
CV1 50N 102 202 302 402
CV1 100N 103 203 303 403
CV1 150N 104 204 304 404
CV2 0N 105 205 305 405
CV2 50N 106 206 306 406
CV2 100N 107 207 307 407
CV2 150N 108 208 308 408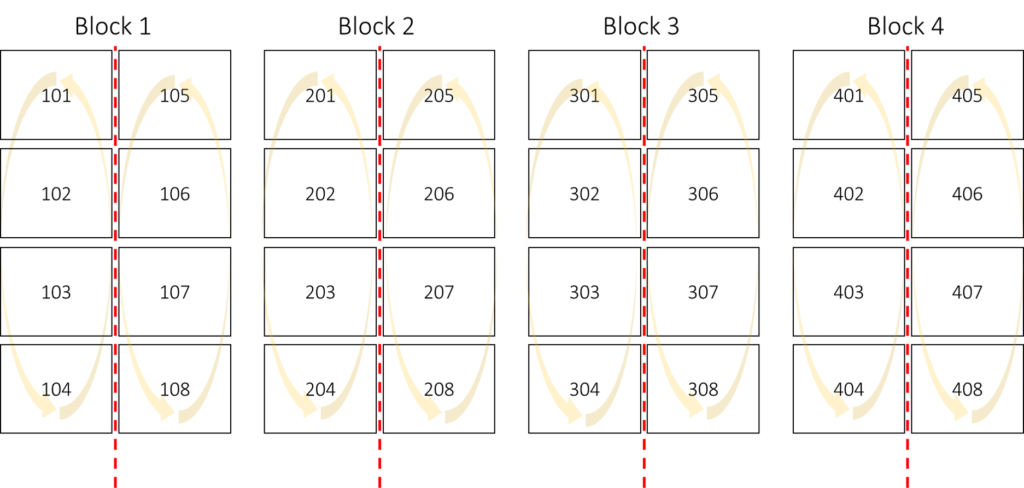
library(dplyr)
set.seed(100)
df_randomized= df %>%
mutate(across(starts_with("Rep"),
~ ave(.x[order(match(Variety,sample(unique(Variety))))],
Variety,FUN=sample)))
df_randomized
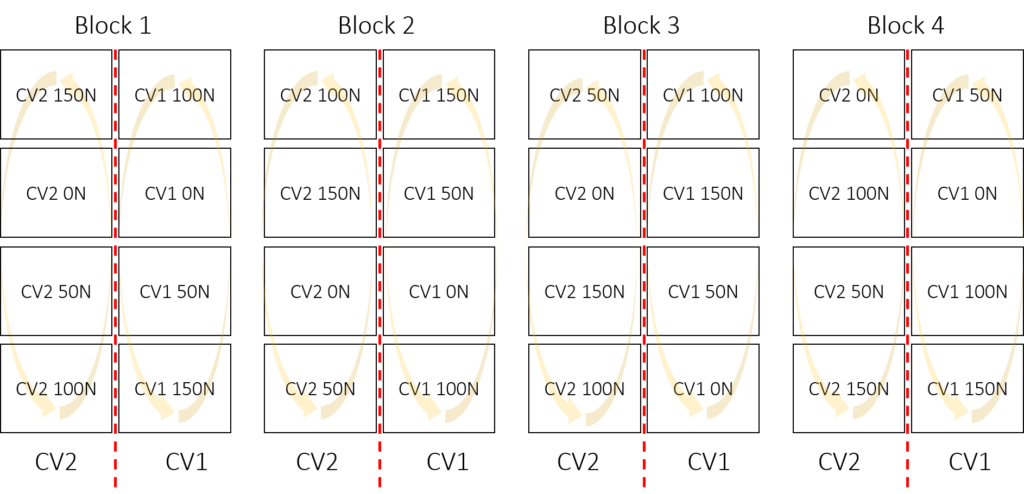
Variety N_rate Rep 1 Rep 2 Rep 3 Rep 4
CV1 0N 106 207 308 406
CV1 50N 107 206 307 405
CV1 100N 105 208 305 407
CV1 150N 108 205 306 408
CV2 0N 102 203 302 401
CV2 50N 103 204 301 403
CV2 100N 104 201 304 402
CV2 150N 101 202 303 404